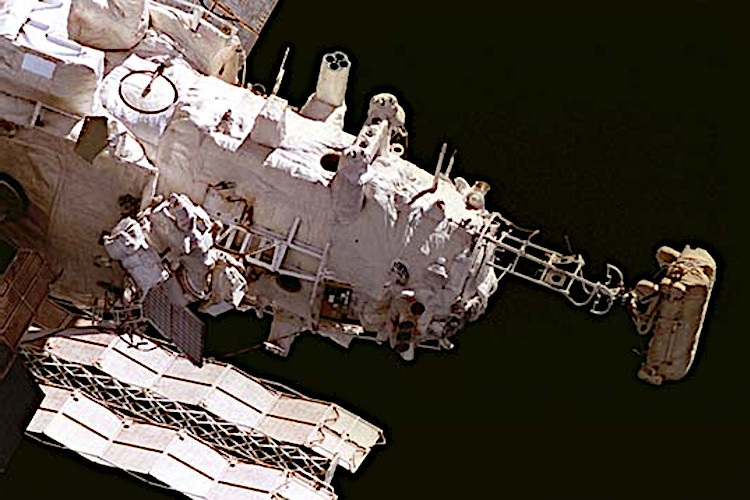
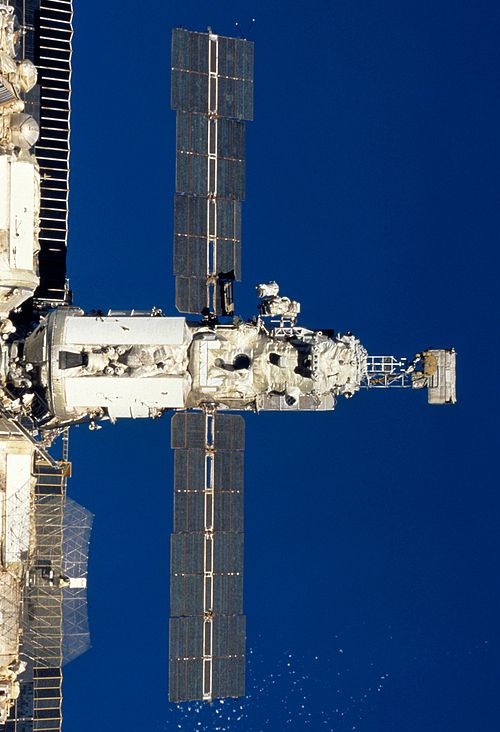
Kvant-2 is connected to the starboard (right) port of the Core Module.


Kvant-2 is connected to the starboard (right) port of the Core Module.

Kvant-2 (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir.
It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket and docked to Mir on December 6.
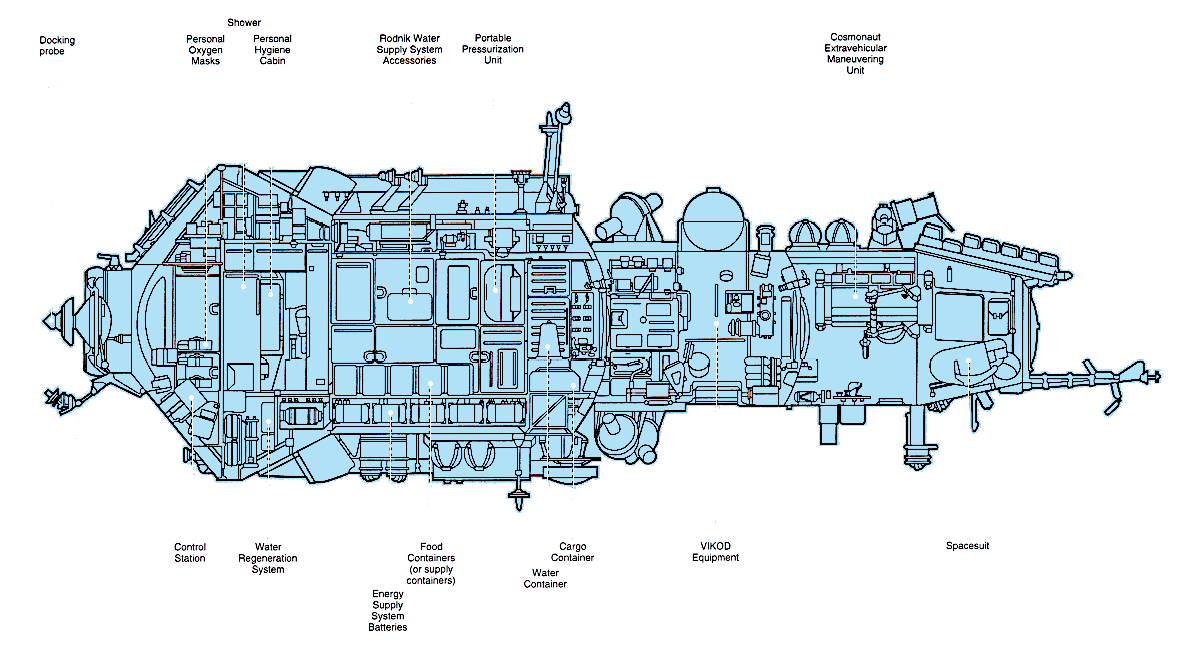
Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft. It was divided into three compartments; an EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment.
The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock.
The addition of an airlock meant that the docking node on the Core Module no longer had to be depressurizing for EVA's. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit.
Kvant-2 had a system for regenerating water from urine and a shower for personal hygiene.It also carried six gyrodynes to augment those already located in Kvant-1.
Length: 12.2 m
Diameter: 4.35 m
Mass: 19,640 kg
Habitable volume: 61.9 m3
Wingspan: 24 m
Configuration:77K (TKS) based module
Scientific equipment included a high-resolution camera, spectrometers, X-ray sensors, the Volna 2 fluid flow experiment, and the Inkubator-2 unit which was used for hatching and raising quail.

Other experiments and equipment were: