
Bishop Airlock is berthed to the end port of Node 3. (Tranquility)

Bishop Airlock is berthed to the end port of Node 3. (Tranquility)

The Bishop Airlock is a commercially funded module built by Nanoracks, Thales Alenia Space, and Boeing. It is used to deploy CubeSats, small satellites, and other external payloads for NASA, Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), and other commercial and governmental customers.

It can also be used to support external experimental payloads and to dispose large pieces of trash from the ISS.
The airlock was named bishop after the similar looking chess piece.
It was launched to the ISS on 6 December 2020 (mission CRS-21) in a SpaceX dragon 2 cargo craft.
The airlock is normally berthed to the port end of the Tranquility module and operated by the Station Arm. It can also be temporarily attached to the Mobile Base System for movement along the main station truss.
References: Airlock Overview, Nanoracks, Wikipedia
The Nanoracks Company has an agreement with NASA to send payloads from academic and private sources for installation on the ISS' experiment racks or deployment from the equipment airlock in the Japanese Kibō module.
Limitations on NASA's use of the JAXA facility created a bottleneck, prompting Nanoracks to develop their own airlock to increase satellite and experiment deployment capabilities.
NASA can also use the airlock to dispose of trash. Station crew place their trash in the airlock and the trash would then be thrown out and burn up in Earth's atmosphere. This would help out the chronic problem of having to keep trash inside all of the modules for months at a time while waiting for a cargo spacecraft to be de-orbited to dispose of the trash.
A Space Act Agreement between NASA and Nanoracks to develop a private airlock was signed in May 2016, and the Nanoracks–Boeing plan to build and launch the module was approved in February 2017.
It was originally manifested to launch on SpaceX CRS-19 in late 2019 but was later re-manifested to launch on SpaceX CRS-21.
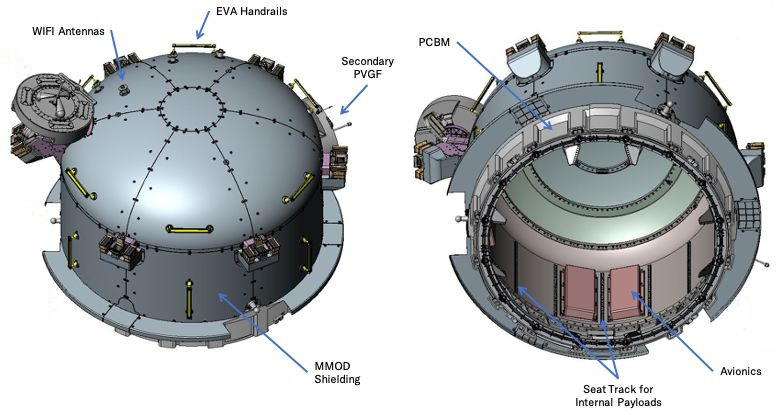
The airlock doesn't have any hatches. When berthed to the Tranquility module it can be pressurised and loaded with small satellites or experiments. It is then de-pressurised and un-berthed using the station arm. The satellites or experiments can then be deployed.
The airlock and its contents can also be to be attached to the Mobile Base System and carried along the main truss.
Typical Airlock Sortie for satellite deployment is as follows:
The airlock is a four-cubic meter bell-shaped canister that is normally berthed to the port end of the Tranquility module.
It does not have hatches but is moved by the Canadarm2 on or off the station's berthing port. The second grapple fixture allows the airlock to be attached to the Mobile Base System.
Mass: 1,059 kg
Height: 1.8 m
Diameter: 2.014 m
Volume - Pressurized: 3.99 m3